- Dec 20, 2019
- 3,833
- 116
You’re reading yet another news article on abortion. It’s all making sense – until they start throwing in terms you have to keep stopping the article to Google. What is an induced abortion? Is that different than a regular abortion? What about a partial-birth abortion? Abortion definitions are crucial to properly understand, learn about and discuss the topic. So what are they?
In legal terms, abortion is the willing termination of a generally healthy and often viable pregnancy.
The definition has varied legally, however. Before 1973, abortion was widely defined as killing, with the American Medical Association, Catholic Church and congress all against the procedure. However, as political tension began to rise, the Supreme Court ruled that a woman’s right to choice was more important than a fetus’s right to life, defining abortion as a fundamental and constitutional right to bodily autonomy.
In 2022, the Supreme Court redefined the right to abortion again in Dobbs v. Jackson. The court stated that linking abortion to a right to autonomy or to “define one’s concept of existence” would also license fundamental rights to “illicit drug use, [or] prostitution.” Therefore, abortion is currently considered to be a nonessential procedure that ends a pregnancy.
In medical terms, an abortion is a chemical/medical or surgical procedure to end a pregnancy. This does not include instances of ectopic pregnancy, which is a life-threatening and nonviable pregnancy that requires a different procedure than abortion called a laparoscopy.
A medical abortion, otherwise known as a chemical abortion or the abortion pill, is the ending of a pregnancy in the first trimester through a two-pill regimen. It accounts for over half of all abortions in the United States. The first pill, mifepristone, blocks a hormone called progesterone. This is necessary for a baby to continue life in the womb. Without it, the fetal heartbeat stops, along with its development and growth. The second pill, misoprostol, is intended to induce labor in pregnant women. It is used in first-term medical abortions or second-term labor induction abortion.
Essentially, misoprostol causes labor and delivery through active contractions. This process is the fastest-growing method of abortion and is even available online to some people, but it also comes with the highest risk of complications (roughly 80 percent).
A surgical abortion, also known as a D&E or vacuum aspiration abortion, is a procedure that ends the pregnancy through manually dilating the cervix and removing the fetus. This is most often performed in the second and third trimester and typically requires a hospital stay and anesthesia or epidural.
The procedure begins with medical or manual dilation the day before to prepare the body for an early delivery. Then, a doctor will remove the fetus in pieces with forceps and a suction device. This is a less common abortion procedure but still accounts for around 40 percent of abortions.
Abortion Pill Reversal (or APR) is a safe and effective treatment for women who regret taking the first abortion pill. It works by providing progesterone, a hormone that mifepristone blocks. If done in time, it can reverse the effects of the first abortion pill and save the pregnancy.
The term “abort” means to completely carry out the abortion of a fetus through removing necessary nutrients and protection from the baby and delivering it from the womb. It is also defined as the process of intentionally miscarrying.
The term “pro-life” means to believe in and advocate for life, most prominently in the womb. Pro-lifers are in favor of inalienable human rights from when life begins at conception to natural death.
But pro-life work was never about solely banning abortion; it actually began far before the political and legal force of Roe v. Wade in the 1970s. Dating back to midivil times, abortion was sought by women and families due to poverty and shame. It was never about female empowerment or reproductive healthcare. It was about fear. This trend continued into the 1900s, where abortion continued to be illegal, but many states didn’t enforce the bans. Unfortunately, abortions never address the actual problem in unplanned pregnancy: that women feel shamed by the church and fearful their circumstances will become worse with a baby.
What women really need is a loving church, access to resources and a man willing to step up and be a good father. Instead, we gave them abortion.
The pro-life movement sees abortion not only as killing, but also as an unhealthy choice for women worried about their pregnancy. When Roe was ruled, now overturned by Dobbs, pro-life proponents have been campaigning for a better life for women and their babies. That’s what the pro-life movement is about.

These topics are also a part of advocating for life:
“Anti-abortion” is a term coined by the pro-choice movement. Simply put, anti-abortion means someone who is against the practice of abortion. While it’s true that pro-life advocates are against abortion, the term excludes large areas of pro-life advocacy. Therefore, it’s not commonly used by anyone other than politically-charged statements.
“Pro-choice’ means to believe abortion is morally and legally acceptable in most or all circumstances. Someone who is pro-choice thinks that a woman’s right to choose abortion is above a fetus’s right to live. Some abortion-rights supporters are divided as to the types of abortion services that should be available under different circumstances, including periods in the pregnancy such as late-term abortions.
Abortion advocates are also divided on when personhood begins. Some believe abortion is ethically acceptable no matter how human the baby in the womb is. This goes directly against human rights and a Constitutional right to life. On the other hand, some argue that a fetus isn’t human. This gives a woman the right to terminate the pregnancy without “killing.” But there are many factors indicating otherwise.
For one: life ends when the heart stops beating. Why is life any different when the heart starts beating at 6 weeks in the womb? At the very least, shouldn’t life begin the same way it’s considered to end?
Secondly: abortion is different than birth control because an unfertilized egg can stay that way forever. But, a fertilized and implanted egg will continue growing until it is interfered with, much like a person out of the womb.
“Anti-life” is similar to pro-choice. To be anti-life is to believe that the choice to abortion triumphs life in the womb. This term is not often used because it generalizes, similarly to the anti-abortion term.
Partial-birth abortion, also called intact dilation and extraction is a method of late-term surgical abortion. It is used when a standard D&E abortion isn’t effective because the fetus is too far along and its bones and limbs are too strong. It begins with dilating a mother’s cervix over several days, which carries major risk of infection and preterm births later in life.
Once the labor has begun, a doctor delivers most of the baby. After the head is outside of his mother’s body, the doctor then aborts it by dismembering and compressing the body and skull, killing it.
Thankfully, this procedure is banned in the United States and is legally considered infanticide when not done because of the health of the mother. But, a shocking third of Americans still think partial birth abortion should be legal.
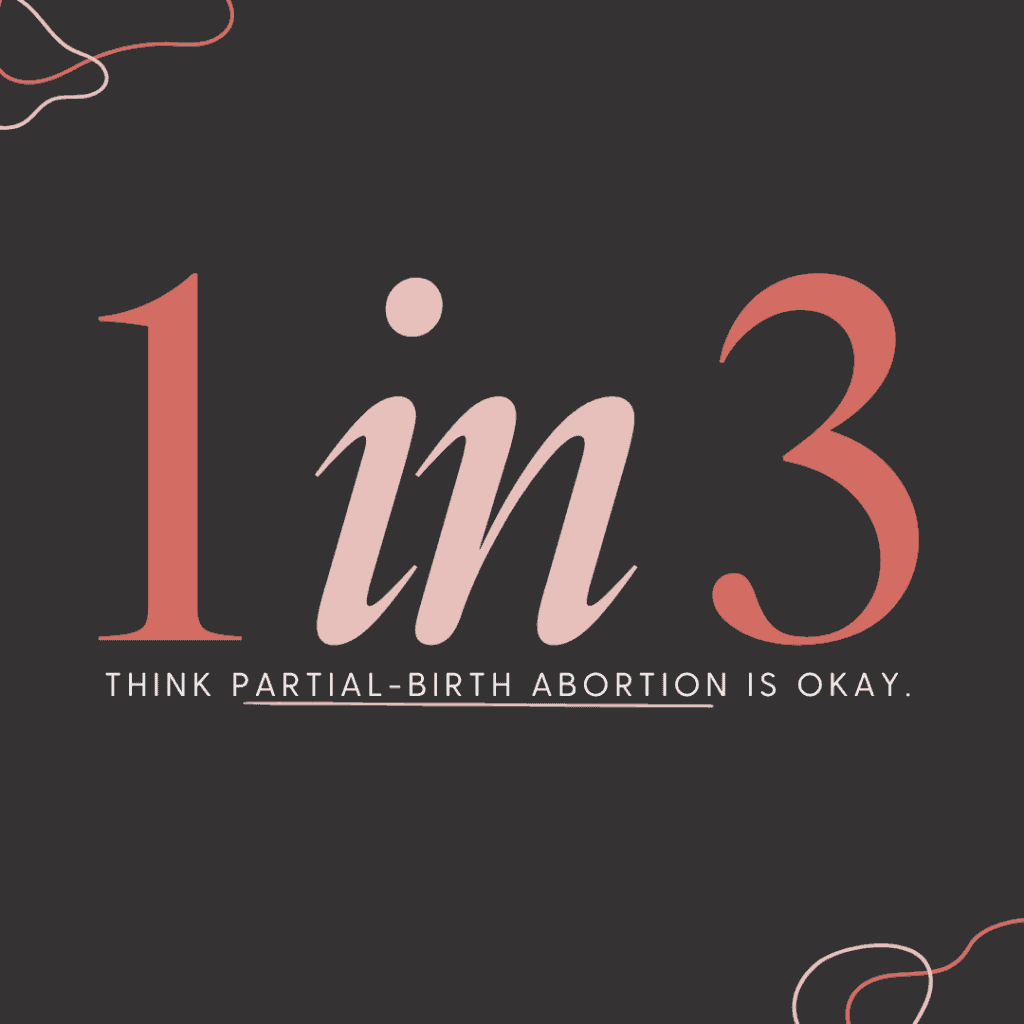
A spontaneous abortion is the natural loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation. It is a type of unintentional miscarriage, and often referred to as miscarriage to avoid connection with induced/intentional abortions.
A missed abortion is a type of spontaneous abortion or miscarriage. It occurs without significant symptoms like pain or contractions. Because there are no contractions, the mother’s body doesn’t realize the baby is no longer alive, and needs a procedure to remove the pregnancy.
Induced abortion is a term that defines intentionally ending a pregnancy in order to cause the death of a fetus.
Medically-induced abortions, also called chemical abortions, use a two-pill combination to stop the baby’s development and expel it from the mother’s body. Surgically-induced abortions (after 16 weeks) require a 2-3 night stay in a hospital. It often includes some form of labor and delivery, and even takes place in the hospital’s maternity ward.
Therapeutic abortion is a procedure that ends a pregnancy to keep the health of the mother intact.
An elective abortion, also called a voluntary abortion, is the interruption and ending of a pregnancy with no medical reason. The overwhelming majority – around 99 percent – of abortions are elective abortions.
The post Guide to Abortion Definitions & Language appeared first on Focus on the Family.
Continue reading...
General Abortion Definitions

Legal Definition of Abortion
In legal terms, abortion is the willing termination of a generally healthy and often viable pregnancy.
The definition has varied legally, however. Before 1973, abortion was widely defined as killing, with the American Medical Association, Catholic Church and congress all against the procedure. However, as political tension began to rise, the Supreme Court ruled that a woman’s right to choice was more important than a fetus’s right to life, defining abortion as a fundamental and constitutional right to bodily autonomy.
In 2022, the Supreme Court redefined the right to abortion again in Dobbs v. Jackson. The court stated that linking abortion to a right to autonomy or to “define one’s concept of existence” would also license fundamental rights to “illicit drug use, [or] prostitution.” Therefore, abortion is currently considered to be a nonessential procedure that ends a pregnancy.
Medical Definition of Abortion
In medical terms, an abortion is a chemical/medical or surgical procedure to end a pregnancy. This does not include instances of ectopic pregnancy, which is a life-threatening and nonviable pregnancy that requires a different procedure than abortion called a laparoscopy.
Medical Abortion Vs. Surgical Abortion Definition
Medical Abortion
A medical abortion, otherwise known as a chemical abortion or the abortion pill, is the ending of a pregnancy in the first trimester through a two-pill regimen. It accounts for over half of all abortions in the United States. The first pill, mifepristone, blocks a hormone called progesterone. This is necessary for a baby to continue life in the womb. Without it, the fetal heartbeat stops, along with its development and growth. The second pill, misoprostol, is intended to induce labor in pregnant women. It is used in first-term medical abortions or second-term labor induction abortion.

Essentially, misoprostol causes labor and delivery through active contractions. This process is the fastest-growing method of abortion and is even available online to some people, but it also comes with the highest risk of complications (roughly 80 percent).
Surgical Abortion
A surgical abortion, also known as a D&E or vacuum aspiration abortion, is a procedure that ends the pregnancy through manually dilating the cervix and removing the fetus. This is most often performed in the second and third trimester and typically requires a hospital stay and anesthesia or epidural.
The procedure begins with medical or manual dilation the day before to prepare the body for an early delivery. Then, a doctor will remove the fetus in pieces with forceps and a suction device. This is a less common abortion procedure but still accounts for around 40 percent of abortions.
Abortion Pill Reversal
Abortion Pill Reversal (or APR) is a safe and effective treatment for women who regret taking the first abortion pill. It works by providing progesterone, a hormone that mifepristone blocks. If done in time, it can reverse the effects of the first abortion pill and save the pregnancy.
Abortive/Abort Definition
The term “abort” means to completely carry out the abortion of a fetus through removing necessary nutrients and protection from the baby and delivering it from the womb. It is also defined as the process of intentionally miscarrying.
Pro-Life and Pro-Abortion Definitions

Pro-Life Definition
The term “pro-life” means to believe in and advocate for life, most prominently in the womb. Pro-lifers are in favor of inalienable human rights from when life begins at conception to natural death.
But pro-life work was never about solely banning abortion; it actually began far before the political and legal force of Roe v. Wade in the 1970s. Dating back to midivil times, abortion was sought by women and families due to poverty and shame. It was never about female empowerment or reproductive healthcare. It was about fear. This trend continued into the 1900s, where abortion continued to be illegal, but many states didn’t enforce the bans. Unfortunately, abortions never address the actual problem in unplanned pregnancy: that women feel shamed by the church and fearful their circumstances will become worse with a baby.
What women really need is a loving church, access to resources and a man willing to step up and be a good father. Instead, we gave them abortion.
The pro-life movement sees abortion not only as killing, but also as an unhealthy choice for women worried about their pregnancy. When Roe was ruled, now overturned by Dobbs, pro-life proponents have been campaigning for a better life for women and their babies. That’s what the pro-life movement is about.
What Does Pro-Life Advocacy Include?

These topics are also a part of advocating for life:
- Reproductive Health
- Foster Care and Adoption
- Special Needs
- Human Trafficking
- Combatting Racism
- Alleviating Poverty and Death
- Pregnancy from Rape/Sexual Assault
- Immigration & Refugees
- End of Life/Hospice Care
Anti-Abortion Meaning
“Anti-abortion” is a term coined by the pro-choice movement. Simply put, anti-abortion means someone who is against the practice of abortion. While it’s true that pro-life advocates are against abortion, the term excludes large areas of pro-life advocacy. Therefore, it’s not commonly used by anyone other than politically-charged statements.
Pro-Choice Definition
“Pro-choice’ means to believe abortion is morally and legally acceptable in most or all circumstances. Someone who is pro-choice thinks that a woman’s right to choose abortion is above a fetus’s right to live. Some abortion-rights supporters are divided as to the types of abortion services that should be available under different circumstances, including periods in the pregnancy such as late-term abortions.
Abortion advocates are also divided on when personhood begins. Some believe abortion is ethically acceptable no matter how human the baby in the womb is. This goes directly against human rights and a Constitutional right to life. On the other hand, some argue that a fetus isn’t human. This gives a woman the right to terminate the pregnancy without “killing.” But there are many factors indicating otherwise.
For one: life ends when the heart stops beating. Why is life any different when the heart starts beating at 6 weeks in the womb? At the very least, shouldn’t life begin the same way it’s considered to end?
Secondly: abortion is different than birth control because an unfertilized egg can stay that way forever. But, a fertilized and implanted egg will continue growing until it is interfered with, much like a person out of the womb.
Anti-Life Meaning
“Anti-life” is similar to pro-choice. To be anti-life is to believe that the choice to abortion triumphs life in the womb. This term is not often used because it generalizes, similarly to the anti-abortion term.
Abortion Procedure Definitions

Partial Birth Abortion Definition
Partial-birth abortion, also called intact dilation and extraction is a method of late-term surgical abortion. It is used when a standard D&E abortion isn’t effective because the fetus is too far along and its bones and limbs are too strong. It begins with dilating a mother’s cervix over several days, which carries major risk of infection and preterm births later in life.
Once the labor has begun, a doctor delivers most of the baby. After the head is outside of his mother’s body, the doctor then aborts it by dismembering and compressing the body and skull, killing it.
Thankfully, this procedure is banned in the United States and is legally considered infanticide when not done because of the health of the mother. But, a shocking third of Americans still think partial birth abortion should be legal.
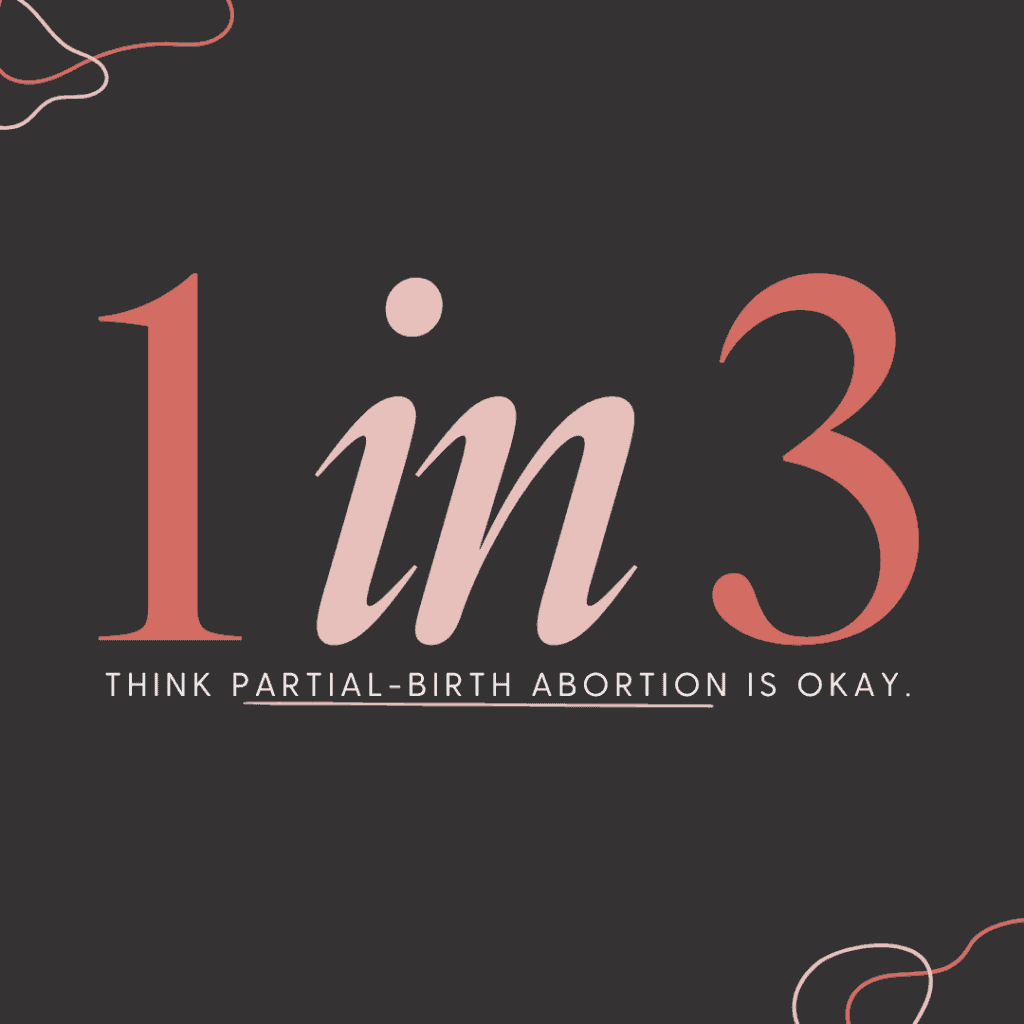
Spontaneous Abortion Definition
A spontaneous abortion is the natural loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation. It is a type of unintentional miscarriage, and often referred to as miscarriage to avoid connection with induced/intentional abortions.
Missed Abortion Definition
A missed abortion is a type of spontaneous abortion or miscarriage. It occurs without significant symptoms like pain or contractions. Because there are no contractions, the mother’s body doesn’t realize the baby is no longer alive, and needs a procedure to remove the pregnancy.
Induced Abortion Definition
Induced abortion is a term that defines intentionally ending a pregnancy in order to cause the death of a fetus.
Medically-induced abortions, also called chemical abortions, use a two-pill combination to stop the baby’s development and expel it from the mother’s body. Surgically-induced abortions (after 16 weeks) require a 2-3 night stay in a hospital. It often includes some form of labor and delivery, and even takes place in the hospital’s maternity ward.
Therapeutic Abortion Definition
Therapeutic abortion is a procedure that ends a pregnancy to keep the health of the mother intact.
Voluntary Abortion or Elective Abortion Definition
An elective abortion, also called a voluntary abortion, is the interruption and ending of a pregnancy with no medical reason. The overwhelming majority – around 99 percent – of abortions are elective abortions.
The post Guide to Abortion Definitions & Language appeared first on Focus on the Family.
Continue reading...



