Since Roe is no more, the reasons for abortion are coming into the political spotlight. Many states are currently limiting access to abortion, while others are actually expanding abortion access post-Dobbs. It presents the opportunity for new ways to combat abortion, including the question: what if we shift our mindset by addressing the root causes of abortion instead of abortion itself? Could we more efficiently direct our support and completely fill the need for abortion, all while it’s still legal? The ultimate pro-life goal shouldn’t be to ban abortion; it should be to support new mothers and families so well, the need for abortion doesn’t even exist. We want women to confidently choose life.
Many unexpectedly pregnant women don’t know their options and turn to abortion as a solution. The majority of women seeking an abortion say the decision comes from multiple themes, fears or worries. Because of this, statistics can vary, and most women will have more than one reason for abortion.
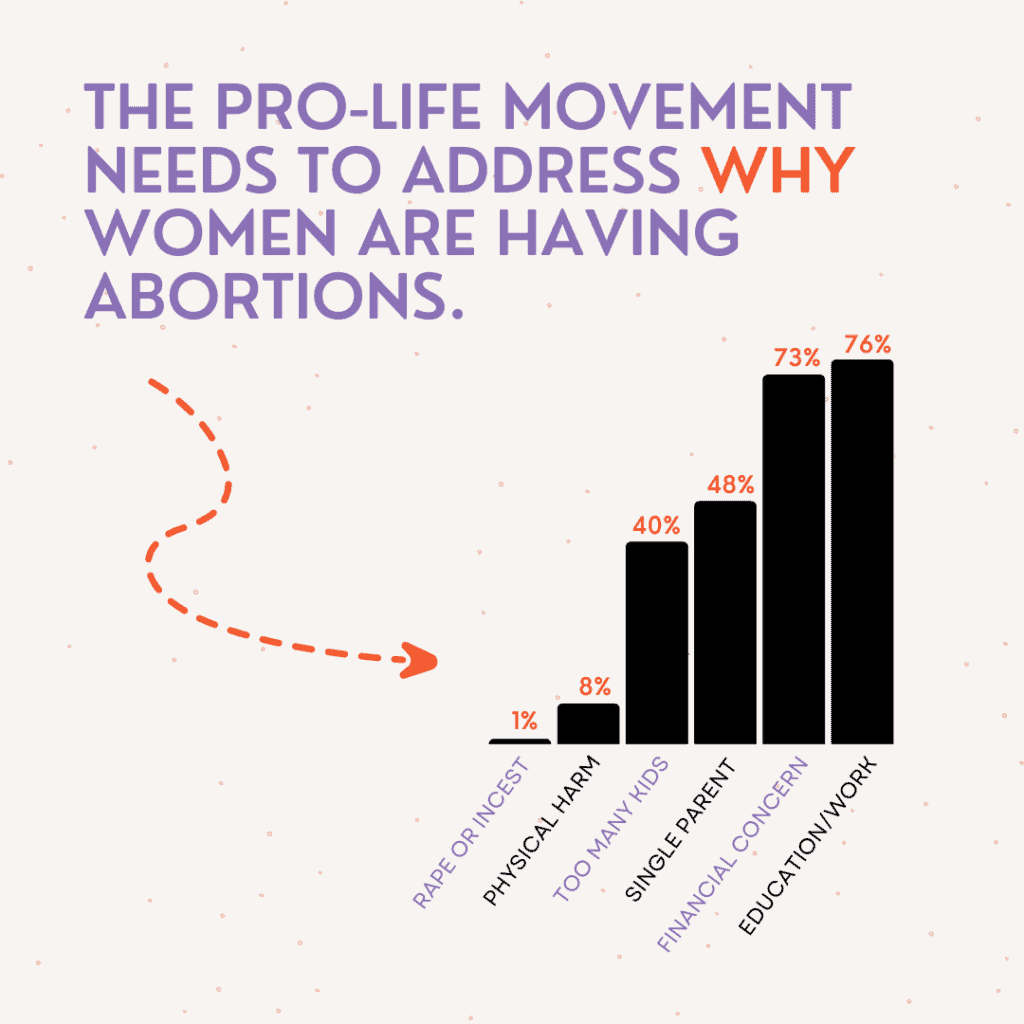
The most common reasons for abortion include:
Around one in four women will have an abortion at some point in their life. Surprisingly, 62 percent of those women affiliate with religion on some level, with an overwhelming majority being of Christian faith.
Over half of women are already mothers and have at least one child when they became unexpectadely pregnant, with 14 percent having two or more kids. Over half are in their twenties – despite a misconception that teens are in the majority (only 12 percent of U.S. abortion patients are younger than 18). 85 percent of women are unmarried.
Additionally, abortion disproportionately effects minority populations. For example, even though women of color represent only 17 percent of the U.S. population, they make up nearly four times that amount of abortions had. On top of that, an overwhelming majority of abortion patients (75 percent) are considered poor or low income.
There are two kinds of abortion that women can get: chemical abortion and surgical abortion.
Chemical abortion, also known as the abortion pill, is currently the fastest-growing form of abortion in the country. It accounts for over half of all abortion procedures, and can occur up to 11 weeks into pregnancy. They also cause the highest amount of complications.
Surgical abortion, or a D&E, is the other form of abortion. It is performed up to birth in some U.S. states, though late-term abortions are not healthy for the mother or baby.
Surgical/late-term abortions and partial-birth abortions are different procedures, both occurring in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. A surgical abortion is invasive and comes with many complications due to the baby’s size. The majority of late-term abortions aren’t due to medical reasons. Instead, the reason is typically that the woman experiences hurdles in receiving an abortion, or that she changes her mind.
Likewise, a partial-birth abortion, or intact dilation and extraction, is the same process but with a few key differences. The labor and delivery process from a D&X is extremely close to that of an actual birth – even to the point of an epidural and delivery in the hospital’s maternity ward. Unfortunately, the child dies right before being completely physically independent from the womb. Though reasons for abortion through D&X vary, they were first created from worry about the side effects from intrauterine dismemberment in D&E abortions (which is now industry standard, though the complications remain just as severe). In cases of miscarriage, parents may choose partial-birth abortion to have the ability to view and grieve their baby’s remains mostly intact.
Partial-birth abortions, however, are currently illegal in most states. The “Partial-Birth Abortion Act” was passed by the U.S. in 2003. According to congress, partial-birth abortions are “a gruesome and inhumane procedure that is never medically necessary and should be prohibited.”
Because fetal abnormalities often don’t present themselves until later in a pregnancy, a surgical abortion is the type of abortion physicians perform for medical reasons. Within the scope of surgical abortion, they either perform a D&E, D&X or suction abortion.
Abortions past 21 weeks of pregnancy don’t make up much percentage of procedures in the United States. However, they still manage to account for over 15,000 procedures each year.

With a suddenly shifting landscape after the Supreme Court handed down the Dobbs v. Jackson decision, abortion bans are changing every day. The types of abortion legal now are both chemical and surgical abortions.
Currently, there are no abortion procedures illegal in all 50 states, so all types of abortion are present in some capacity in the U.S. In individual states, however, many are limiting or banning access to abortion – meaning the only type of abortion legal in those states are in cases of life endangerment. Most also have exceptions for rape or incest.
See here for an up-to-date map of where abortion is legal.
Though the reasons for abortion greatly vary, it comes down to anxieties stemming from readiness, finances, education or single motherhood. If the pro-life movement does its job, we can address those concerns at their core with support and love, making abortion unthinkable whether it’s legal or not.
The post Reasons for Abortion: Stats & Demographics appeared first on Focus on the Family.
Continue reading...
What is the Main Reason for Abortion?
Many unexpectedly pregnant women don’t know their options and turn to abortion as a solution. The majority of women seeking an abortion say the decision comes from multiple themes, fears or worries. Because of this, statistics can vary, and most women will have more than one reason for abortion.
The most common reasons for abortion include:
- Education or work – 76 percent
- Financial concern – 73 percent
- Fear of single motherhood – 48 percent
- Completed childbearing/don’t want more children – 40 percent
- Emotionally unprepared – 19 percent
- Fetal health concern – 8 percent
- Influence from family/friends – 5 percent
- Rape or incest – 1 percent

Who Gets Abortions?
Around one in four women will have an abortion at some point in their life. Surprisingly, 62 percent of those women affiliate with religion on some level, with an overwhelming majority being of Christian faith.
Over half of women are already mothers and have at least one child when they became unexpectadely pregnant, with 14 percent having two or more kids. Over half are in their twenties – despite a misconception that teens are in the majority (only 12 percent of U.S. abortion patients are younger than 18). 85 percent of women are unmarried.
Additionally, abortion disproportionately effects minority populations. For example, even though women of color represent only 17 percent of the U.S. population, they make up nearly four times that amount of abortions had. On top of that, an overwhelming majority of abortion patients (75 percent) are considered poor or low income.
What Are The Types of Abortion?

There are two kinds of abortion that women can get: chemical abortion and surgical abortion.
Chemical abortion, also known as the abortion pill, is currently the fastest-growing form of abortion in the country. It accounts for over half of all abortion procedures, and can occur up to 11 weeks into pregnancy. They also cause the highest amount of complications.
Surgical abortion, or a D&E, is the other form of abortion. It is performed up to birth in some U.S. states, though late-term abortions are not healthy for the mother or baby.
What Are The Reasons for Partial Birth or Late-Term Abortions?
Surgical/late-term abortions and partial-birth abortions are different procedures, both occurring in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. A surgical abortion is invasive and comes with many complications due to the baby’s size. The majority of late-term abortions aren’t due to medical reasons. Instead, the reason is typically that the woman experiences hurdles in receiving an abortion, or that she changes her mind.
Likewise, a partial-birth abortion, or intact dilation and extraction, is the same process but with a few key differences. The labor and delivery process from a D&X is extremely close to that of an actual birth – even to the point of an epidural and delivery in the hospital’s maternity ward. Unfortunately, the child dies right before being completely physically independent from the womb. Though reasons for abortion through D&X vary, they were first created from worry about the side effects from intrauterine dismemberment in D&E abortions (which is now industry standard, though the complications remain just as severe). In cases of miscarriage, parents may choose partial-birth abortion to have the ability to view and grieve their baby’s remains mostly intact.
Partial-birth abortions, however, are currently illegal in most states. The “Partial-Birth Abortion Act” was passed by the U.S. in 2003. According to congress, partial-birth abortions are “a gruesome and inhumane procedure that is never medically necessary and should be prohibited.”
What Type of Abortion is Done for Medical Reasons?
Because fetal abnormalities often don’t present themselves until later in a pregnancy, a surgical abortion is the type of abortion physicians perform for medical reasons. Within the scope of surgical abortion, they either perform a D&E, D&X or suction abortion.
Abortions past 21 weeks of pregnancy don’t make up much percentage of procedures in the United States. However, they still manage to account for over 15,000 procedures each year.

What Type of Abortion is Still Legal?
With a suddenly shifting landscape after the Supreme Court handed down the Dobbs v. Jackson decision, abortion bans are changing every day. The types of abortion legal now are both chemical and surgical abortions.
Currently, there are no abortion procedures illegal in all 50 states, so all types of abortion are present in some capacity in the U.S. In individual states, however, many are limiting or banning access to abortion – meaning the only type of abortion legal in those states are in cases of life endangerment. Most also have exceptions for rape or incest.
See here for an up-to-date map of where abortion is legal.
Though the reasons for abortion greatly vary, it comes down to anxieties stemming from readiness, finances, education or single motherhood. If the pro-life movement does its job, we can address those concerns at their core with support and love, making abortion unthinkable whether it’s legal or not.
The post Reasons for Abortion: Stats & Demographics appeared first on Focus on the Family.
Continue reading...





