Torah
Level: Basic
• Torah in the narrowest sense refers to the first five books of the Bible
• In a broader sense, Torah includes all Jewish law and tradition
• Torah was given to Moses in written form with oral commentary
• The oral component is now written in the Talmud
• There are additional important writings
The word "Torah" is a tricky one, because it can mean different things in different contexts. In its most limited sense, "Torah" refers to the Five Books of
Moses: Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. But the word "torah" can also be used to refer to the entire Jewish bible (the body of scripture known to non-Jews as the Old Testament and to Jews as the Tanakh or Written Torah), or in its broadest sense, to the whole body of Jewish law and teachings.
Written Torah
To Jews, there is no "Old Testament." The books that Christians call the New Testament are not part of Jewish scripture. The so-called Old Testament is known to us as Written Torah or the Tanakh.
This is a list of the books of Written Torah, in the order in which they appear in Jewish translations, with the Hebrew name of the book, a translation of the Hebrew name (where it is not the same as the English name), and English names of the books (where it is not the same as the Hebrew name). The Hebrew names of the first five books are derived from the first few words of the book. The text of each book is more or less the same in Jewish translations as what you see in Christian bibles, although there are some occasional, slight differences in the numbering of verses and there are some significant differences in the translations.






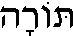

 :
: